Network from the very beginning has been growing in a huge way, and today, there are billions of devices stay online, but that just is the another beginning, IoT, self-driving car, and many new concepts show up in front of us, we knows, another network boost is coming, but IP address shortage already called out many year ago, even though, there are still no much motion to switch IPv4 to IPv6, maybe that is because new cost can’t bring much business, and old IP plan can still stand in current situation.
With new network booming background, For sure, IPv4 can’t full-filled our requirement any more. What about enterprise service structure? it is already a challenge to serve user well in current situation, especially for latency, they won’t stand on new network, too, and even for enterprise, they want just deploy service clouds internally, which will make them stay further with customers, and network infrastructure can’t tolerate such waste, especially for duplicate contents.
New rules, New concepts should stand out. IPv6 have a huge address space, and still with address saving property built-in, it will come on stage. Edge Computing, deploy service clouds at network access layer, closer to end user, which can fix latency issue, what’s more, bandwidth at back-bone network saved, it is a attractive solution for enterprises, and gain more and more popular in recent years. In the rest of this post, I will talk some design about edge computing, and how it will deploy in IPv6 network.
IPv6 introduction
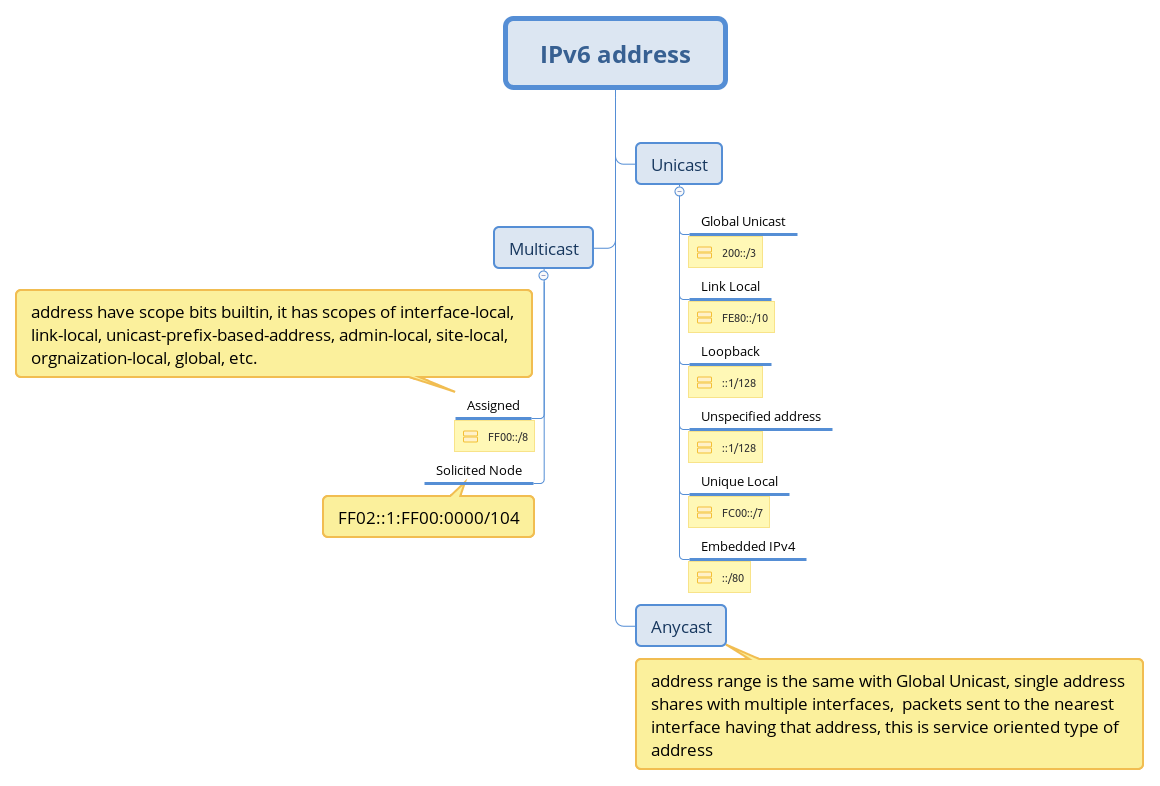
There are several address saving properties in IPv6:
1, all addresses in subnet are usable, no address reserved for network ID and broadcast, and there is not broadcast address in IPv6;
2, ANYCAST, which multiple interface can share one single global unicast address, router can help to forward packets to the nearest interface;
3, all router may start to use link-local address, which can enhance back-bone network security, and lots of global unicast address saved.
Instead of ARP, IPv6 use ICMP to request MAC address, and multicast is used instead of broadcast in IPv4, and multicast has scope bit defined which limit how far packets can reach.
Edge Computing
when we surf internet, the key facts effect our experience are bandwidth, network speed, and latency, ISPs can enhance network infrastructure to add more bandwidth, and network speed, but the distance between enterprise services and users is still there, so latency can’t become less efficiently, how can we improve it? move enterprise services closer to users, that is where edge computing come from.
Back-bone network is consists of core layer, distributed layer, and access layer. Access layer is closest to user, which is called the last 1KM, when we deploy edge clouds at access layer as services interface to users for enterprises, it has many benefits:
1, latency can be reduced very efficiently;
2, many things can be handled at access layer, users’ requests don’t need to send to back-bone network every time, especially for static contents, like images, video, web pages, and etc, which can save many bandwidth for back-bone network, and avoid many duplicated contents waste back-bone network’s capability;
3, some location, user group, culture difference, local based services, it can handle efficiently.
we already know so many advantages in edge computing, but how can we implement it? based on basic concept, it should have huge number of edge service clouds deployed at access layer, how each edge clouds and enterprise service clouds sync efficiently could be a challenge. So in the rest of post, I am going to talk about it.
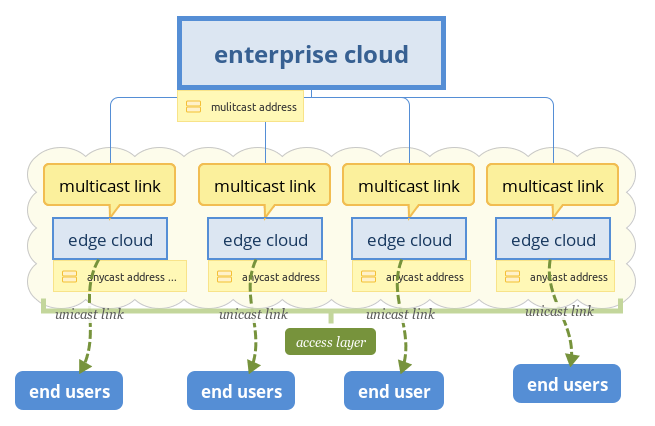
First, let’s imagine user requests service, each edge service cloud reply its requests locally in IPv4 network, how can we setup this network?
1, each edge service cloud needs at least one public address;
2, ISP needs to add some extra DNS entries for each edge cloud;
3, domain name can not be the same with enterprise service clouds, or there will be some conflicts.
Design edge cloud in this way will be tedious, a big public address pool is needed for each enterprise, ISP have many network confiuration to do, and user have to enjoy services from different interface, no one is really happy about it.
In previous section, I introduced IPv6, ANYCAST is very applicable in this scenario, every edge clouds, including enterprise clouds, can share the same global unicast address, one DNS entry can rule them all, router will route packets to the nearest server, which is very fit to edge computing, and to user, they don’t sense edge cloud’s existence, what they feel is better network experience. I think anycast is the best choice, which can save a large number of IP addresses, and simplify network configuration and maintain.
After talking about user interface in edge computing, let’s discuss about data sync between enterprise cloud and edge cloud, now.
one option is IPSEC, each edge cloud have a VPN channel with enterprise cloud, which can ensure data security. This option is widely used in enterprises currently, especially site-to-site VPN connection, but VPN has its own issue, performance is big one, enterprise cloud can’t have too much VPN channels with edge cloud, and enterprise’s intranet is used by employee only, which is not the same with services have billions of users, and VPN itself needs public address at each end, it conflicts with ANYCAST strategy, enterprise cloud’s stress will not relief, and the total cost cloud be even higher.
In IPv6’s multicast address, you may notice it have some extension bit, like scope, it can be used in this situation. What if we have all the edge clouds and enterprise cloud in a singe multicast group, will this thing be simplified? absolutely. Enterprise cloud just need to multicast one stream, every edge clouds can receive it, and bandwidth at back-bone widely saved, it is very applicable to static content, like image, video, web pages, and etc, most importantly, this can save much enterprise cloud’s cost.
Beside static contents, there are some local specific behind each edge cloud, which users share locally, so something like unicast is needed, I think implement it based on multicast framework is not difficult, we can add subscribe to local specific contents, like one TV channel, only one is watching.
Security
ANYCAST as interface to user, enterprise cloud is totally hidden from user, and there is no way for user to reach enterprise cloud directly, the only way is through edge cloud, so enterprise servers’ security is better enhanced. If there are attacks exist, edge cloud is located at access layer, damages will be minimized, it won’t widely effect the whole network like today.
Multicast as a way for data sync between edge cloud and enterprise cloud, which isolated from unicast network, and multicast have scope, which ensure data in channel won’t leak behind access layer, hackers can’t sneak anything just stay at home.
In IPv6 network, what I heard but not confirmed, it will start to use private routing, which means all the routers don’t use global unicast address, but link local address, it restricts the scope where routers could be reached, if it is true, all routers above access layer can’t be reached from end users, that is a big step in security enhancement. It reminds me of IPv4 network, traceroute command can tell how many routers in the path from initial host to destination host, which proved is big security issue, and it was forbidden at routers, and many features which cause security issue are forbidden, too, like ICMP, I don’t think it is the right direction to just forbidden all, which will cause security issues, private routing can fix these security issue smartly. Routers’s scope itself is limited, who they want to be reached are their neighbors, so they don’t need to use global unicast addresses, which can be reached globally, link local address can define its scope perfectly. Based on IPv4 routing design, switch to private routing the modification is not much, it totally doable, I hope it will be the next generation of routing.
And the next thing is NAT, many people believe it is more secure to hide behind NAT, but it is not whole true. Many network performance issues are because of NAT, especially for gateway, it need to translate between public address and private address packet by packet, and do many modification to packets for hosts behind, that burden will limit its throughput, and be very easy to choose as attack point, and for hosts, it definitely need to access internet, that means they still stay online, it is not real safety. In IPv6 network, every host has global unicast address, which does not mean it is less safe that NAT, if host does not have port opening, outside network could not be reached, and gateway can still do many thing for hosts, like forward packets to hosts want only, hosts can just subscribe what they want from gateway, all the other gateway will filter out for hosts, it is the same security level to NAT, but no packets modification, no address translation, and better performance. So in IPv6 network, network security is not a issue, but better, just every host have global unicast address, which is very easy to expose users’ ID, it is better for government to do surveillance, though.
Conclusion
Edge computing open a new door for market which require extreme low-latency reaction, like the coming self-driving car, VR, and etc.
It is the future where everywhere on internet is cloud, the current centralized services deployment will destined to be replaced by decentralized cloud, which is faster, real-time, and better.
