This article I like to introduce some technical details about how firewall system block Youtube service, and based on the analysis of filter mechanism, I will try to tell you how to break it.
Here we go.
In last article, I tried to analysis how firewall system block Google, which is
-
IP address filtering
-
keywords filtering
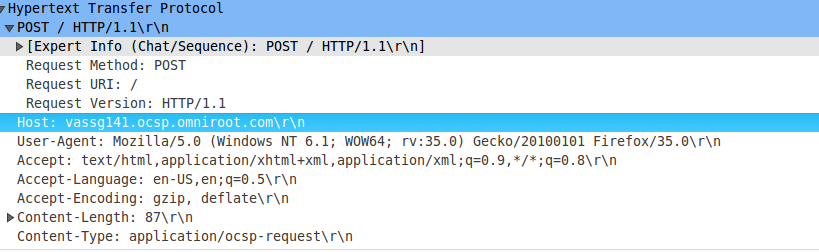
these two mechanism also work here, but there are a little difference in keywords filtering, when you visit Google’s search service, firewall system check GET/POST packets for your search keywords, it will trigger firewall system send RST packet to your device if some sensitive information found, for Youtube, firewall system still check GET/POST packets, but different header field in HTTP header, which is HOST, this header field is required in every HTTP request packets, its value is target’s domain name, firewall system can known which domain name you want to visit by checking this field-value, here it is youtube.com, so it will trigger firewall system send RST to your device.
Filtering Summarize
The youtube service block mechanism: the first step is add youtube severs’ IP addresses into black list, the second step is check HOST header field in HTTP header, which HTTP packet type is GET/POST, if it is youtube.com, fire RST.
there is one question here, if you find a valid youtube server’s IP address, which is not in black list, and you input that IP address in browser, it doesn’t return youtube’s website to you, but Google’s search website. You know, Google has many services, youtube is one of them, that means Google’s IP pool is youtube’s IP pool, too, and it has Gmail, maps, docs, and etc, almost all of these services you can visit from the same server, actually, I don’t know how Google works, and it is not very possible that Google have all the services in the same server, I guess it must have some internal mechanism between Google servers, they can schedule other resources from other servers when they don’t have, and return to user directly, and don’t need user to visit other servers, this can simplify the procedure. In last article, I said when you found a valid Google server’s IP address, and just input that address in browser, Google will return you a search website, which is its default service, how we can visit Google other services from the same server ? from my investigation, this service discrimination lie in header field HOST of HTTP header, that is why firewall system use it to block youtube service, when you just input Google server’s IP address in browser, HOST is the IP address you input, Google don’t know which service you want to access, so it return its default service—-search engine, if you visit its youtube service, HOST field-value is youtube.com, if Gmail, HOST field-value is gmail.google.com, if maps, HOST field-value is maps.google.com, and etc.
you may ask how to make HOST field-value be the target service domain in HTTP header, or how to relate the target service domain with the IP address you specified? In order to answer this question, let’s talk about what exactly happens when you input a URL in browser.
The first thing operator system want to know is where you want to visit, it decode what you input, if it is a IP address, operator system will establish a connection with server with that IP address, and get what you request; if it is domain name, operator system need to translate domain name into IP address, and then, establish a connection, get what you request. how operator system translate domain name into IP address is very import part of this article, so I talk about it in detail, each OS, like windows, Linux, may have a little difference, but the main idea is the same, let’s first talk about Linux, Ubuntu, as a example, when it receive a domain name, where it first send DNS query to depends on the configure file /etc/resolv.conf, by default, the target DNS server is 127.0.0.1, that means it send DNS query to itself, Ubuntu handle DNS in proxy way, one dnsmasq process listens on port 53, which port is reserved for DNS, after dnsmasq receives DNS query, what it first do is check configuration file /etc/hosts, if there is a domain name in this file match domain in DNS query, it will return IP address configured for that domain directly, and no DNS query will send out, if no match, dnsmsq will send DNS query to DNS server configured on default WAN interface, when DNS response receives, it will return to application which is waiting, here it is browser, if no DNS response receives, dnsmasq will try several times till time out.
Windows has a similar mechanism and similar hosts configuration file, it is C:\windows\system32\driver\etc\hosts. You know, for all the forbidden sites in firewall system, the most important thing is avoid send any DNS query out, any IP addresses return from DNS servers inside firewall system are in black list.
Time To Break Restriction
Break restriction 1: For IP address blocking, in previous article, I already said how to find a valid IP address, skip it here.
Break restriction 2: after find a valid IP address, we can’t input it in browser directly, because Google won’t know which service you want to visit, need to do a little trick, configure IP address of domain youtube.com into hosts file, like appending below to host file in your OS:
(replace here with ip you find) youtube.com ytimg.com google.com google.com.hk googlevideo.com
it works at windows OS, but Linux, that is because there is a little different when they search domain in hosts file, windows OS search domain’s suffix, if you configure google.com in hosts file, the target service domains all with suffix google.com, like maps.google.com, docs.google.com, can match in host file, and return IP address succeed, but Linux, it is strict match, that means google.com only match google.com, if the target service domain is maps.google.com, Linux will failed to find a entry in hosts file, that is weird, but it is not so difficult problem, change the match rule in dnsmasq, just several lines of code can fix it, and I will come up later when it is done. Without match rule change in dnsmasq, you still can open youtube site, but when you watch video, it will display error, that is because video’s service domain name is not a fixed one, but with some weird prefix, like r2—xxxx.googlevideo.com, r4—xxxx.googlevideo.com, so match rule in dnsmasq has to be changed before watching video.
And about keywords filter system in firewall, I think we have a way to ignore the RST packet firewall sending, in previous article, I talked about TTL, the TTL value your device receives from firewall system is much different with it from original server, for Linux system, we can fix it in kernel, when connection establishes, TTL value can record in socket structure, and if kernel receives RST, it can compare the TTL in RST with it in socket structure, which can tell whether this RST is send from original server, and I will come up later when it is done.
Conclusion
The usual methods firewall system used to block site accessing are IP filtering and keywords filtering. when we want to break through, the first thing is find a valid IP address, and second is avoid DNS query sending out, and use secure connection if server support, this technical I tested in Windows, Linux, I think IOS, too, just need to know how to configure it.
Fix me if you find some wrong, and drop me email if you have questions.
