Keywords filtering system is one of filtering mechanism in firewall, it can make the connection broken immediately, and the service we visit will stop, one simple example is we search something via Google, browser display connection reset, right after we input the search keywords.
In order to explain how we can fix it up, I introduce some data structure first:
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = tcp_close,
.connect = tcp_v4_connect,
.disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
.accept = inet_csk_accept,
.ioctl = tcp_ioctl,
.init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
.destroy = tcp_v4_destroy_sock,
.shutdown = tcp_shutdown,
.setsockopt = tcp_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = tcp_getsockopt,
.recvmsg = tcp_recvmsg,
.sendmsg = tcp_sendmsg,
.sendpage = tcp_sendpage,
.backlog_rcv = tcp_v4_do_rcv,
.release_cb = tcp_release_cb,
.hash = inet_hash,
.unhash = inet_unhash,
.get_port = inet_csk_get_port,
.enter_memory_pressure = tcp_enter_memory_pressure,
.stream_memory_free = tcp_stream_memory_free,
.sockets_allocated = &tcp_sockets_allocated,
.orphan_count = &tcp_orphan_count,
.memory_allocated = &tcp_memory_allocated,
.memory_pressure = &tcp_memory_pressure,
.sysctl_mem = sysctl_tcp_mem,
.sysctl_wmem = sysctl_tcp_wmem,
.sysctl_rmem = sysctl_tcp_rmem,
.max_header = MAX_TCP_HEADER,
.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
.slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
.twsk_prot = &tcp_timewait_sock_ops,
.rsk_prot = &tcp_request_sock_ops,
.hashinfo = &tcp_hashinfo,
.no_autobind = true,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_tcp_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_tcp_getsockopt,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG_KMEM
.init_cgroup = tcp_init_cgroup,
.destroy_cgroup = tcp_destroy_cgroup,
.proto_cgroup = tcp_proto_cgroup,
#endif
};
Struct proto tcp_prot is the central structure of TCP protocol in Linux kernel, which define in file net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c, all the connection control and packets in/out are hanled by HOOK functions in this structure, like HOOK function backlog_rcv receive packets from layer 3, and deliver them to upper layer.
struct inet_sock {
/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */
struct sock sk;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
struct ipv6_pinfo *pinet6;
#endif
/* Socket demultiplex comparisons on incoming packets. */
#define inet_daddr sk.__sk_common.skc_daddr
#define inet_rcv_saddr sk.__sk_common.skc_rcv_saddr
#define inet_dport sk.__sk_common.skc_dport
#define inet_num sk.__sk_common.skc_num
__be32 inet_saddr;
__s16 uc_ttl;
__u16 cmsg_flags;
__be16 inet_sport;
__u16 inet_id;
struct ip_options_rcu __rcu *inet_opt;
int rx_dst_ifindex;
__u8 tos;
__u8 min_ttl;
__u8 mc_ttl;
__u8 pmtudisc;
__u8 recverr:1,
is_icsk:1,
freebind:1,
hdrincl:1,
mc_loop:1,
transparent:1,
mc_all:1,
nodefrag:1;
__u8 rcv_tos;
__u8 convert_csum;
int uc_index;
int mc_index;
__be32 mc_addr;
struct ip_mc_socklist __rcu *mc_list;
struct inet_cork_full cork;
};
Struct inet_sock maintains network elements of connection established, like IP addresses and ports of foreign and local, TOS value, outgoing device index, etc, and it is embedded in struct sock sk, which is the central structure of socket, and which controls and maintains all the states of connection, we can use inet_sk(sk) call to get struct inet_sock information from struct sock. There are two elements related to TTL in struct inet_sock I like to mention here, uc_ttl is TTL for local machine, TTL in IP header will take its value when send out, if its value is not -1, which is the value when socket init, but we can set its value via ioctl; mc_ttl is TTL for multicasting, for unicast, there is no use, so we can use it to record TTL value received from peer, which can help us to fixup RST attack, when socket init, mc_ttl is set to 1.
#code segement of function inet_create, when socket init.
inet->inet_id = 0;
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
inet->uc_ttl = -1;
inet->mc_loop = 1;
inet->mc_ttl = 1;
inet->mc_all = 1;
inet->mc_index = 0;
inet->mc_list = NULL;
inet->rcv_tos = 0;
Ok, let’s start to dig code to find out how TCP socket works in Linux kernel, to simplify the case, I only talk about receiving diretion.
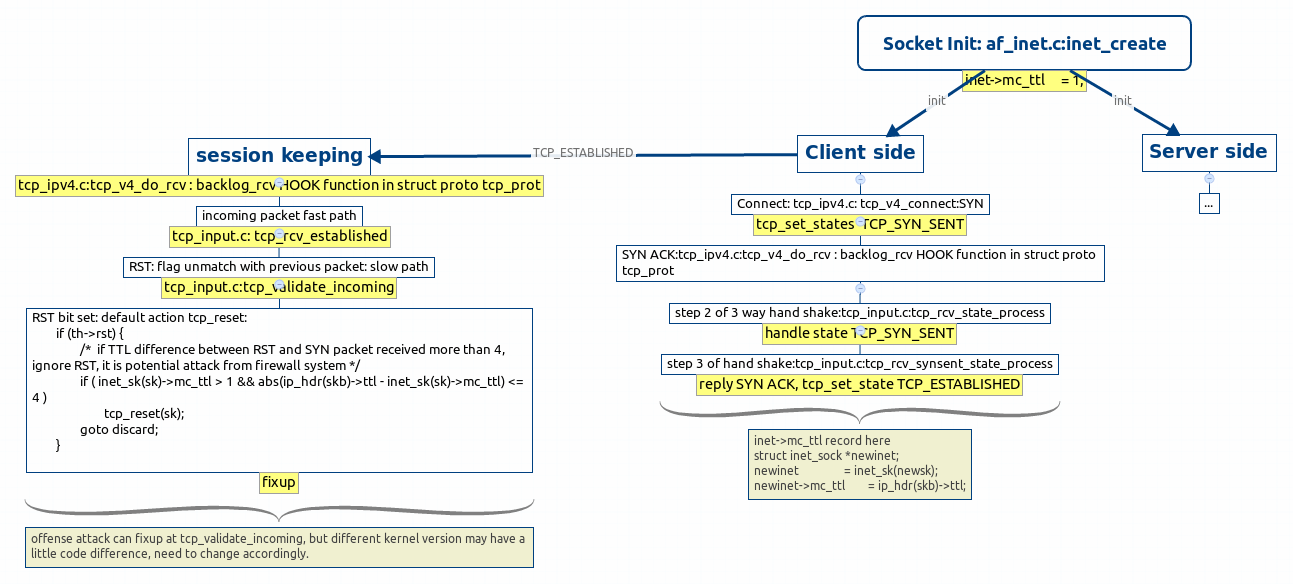
when socket start, we are client, we start the connection, after socket init, 3 way hand shake start:
HOOK function connect, for TCP tcp_v4_connect, send SYN to server, and set TCP socket state to TCP_SYN_SENT;
Server reply SYN ACK, it is handled by HOOK function backlog_rcv, tcp_v4_do_rcv in TCP, it calls tcp_rcv_state_process to deal with state TCP_SYN_SENT;
tcp_synsent_state_process called to handle SYN ACK from server, it send SYN ACK back to server, and set TCP socket state to TCP_ESTABLISHED, if TCP flags server send are not SYN ACK, like RST, it will deal with in different way.
#TTL record in tcp_synsent_state_process
we can record TTL value from server here after tcp state to TCP_ESTABLISHED
# code segement
inet_sk(sk)->mc_ttl = ip_hdr(skb)->ttl;
after connection established, HOOK backblog_rcv will handle stream in fast path under the condition of flag in TCP header match flag in previous packet, it calls tcp_rcv_established, if there is one packet with flag RST recevie, it will obvious make flag unmatch with previous one, and packet will go to slow path, tcp_validate_incoming will be called to handled the exception, which define in net/ipv4/tcp_input.c.
In tcp_validate_incoming, flags checking plays significant role, including RST flag checking.
#code segment of function tcp_validate_incoming
/* Step 2: check RST bit */
if (th->rst) {
/* RFC 5961 3.2 :
* If sequence number exactly matches RCV.NXT, then
* RESET the connection
* else
* Send a challenge ACK
*/
if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq == tp->rcv_nxt)
tcp_reset(sk);
else
tcp_send_challenge_ack(sk, skb);
goto discard;
}
By default, tcp_reset will be called to terminate the connection, if RST flag set.
Defense attack fixup:
#code segment of function tcp\_validate\_incoming
/* Step 2: check RST bit */
if (th->rst) {
/* RFC 5961 3.2 :
* If sequence number exactly matches RCV.NXT, then
* RESET the connection
* else
* Send a challenge ACK
*/
/* if TTL difference between RST and SYN packet received from peer more than 4, ignore RST, it is potential attack */
if (inet_sk(sk)->mc_ttl > 1 && abs(ip_hdr(skb)->ttl - inet_sk(sk)->mc_ttl) > 4)
goto discard;
else if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq == tp->rcv_nxt)
tcp_reset(sk);
else
tcp_send_challenge_ack(sk, skb);
goto discard;
}
Fix me, if you find something wrong in my article, Thanks.
