Layer 3, as we all know, play the most important role in network, it is the main layer which route packets between routers and routers until it reach target host, and which network security apply on.
In this post, I will focus on the basic framework of layer 3, and there are some sub-layers wealth us to dig, too, like nf_conntrack, route, ALG, netfilter, and etc, which designed based on the basic framework, and I will introduce them in later posts.
How packets receving in layer 3 ?
In last post, I mentioned linked list ptype_base, it is layers 3 protocol hook list, protocol hook registered on this list is iterated in API netif_receive_skb, hook function will be called if protocol find on this list.
static struct packet_type ip_packet_type __read_mostly = {
.type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IP),
.func = ip_rcv,
};
static int __init inet_init(void)
{
...
dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type);
...
}
The code segment shows above is defined in file net/ipv4/af_inet.c, it is the IPV4 protocol hook with hook function ip_rcv, which defined in file net/ipv4/ip_input.c.
For IPV6, it is similar:
static struct packet_type ipv6_packet_type __read_mostly = {
.type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IPV6),
.func = ipv6_rcv,
};
static int __init ipv6_packet_init(void)
{
dev_add_pack(&ipv6_packet_type);
return 0;
}
In hook function, it will do some packet header validation, and then packets will be sent to HOOK NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING.
Layer 3 framework
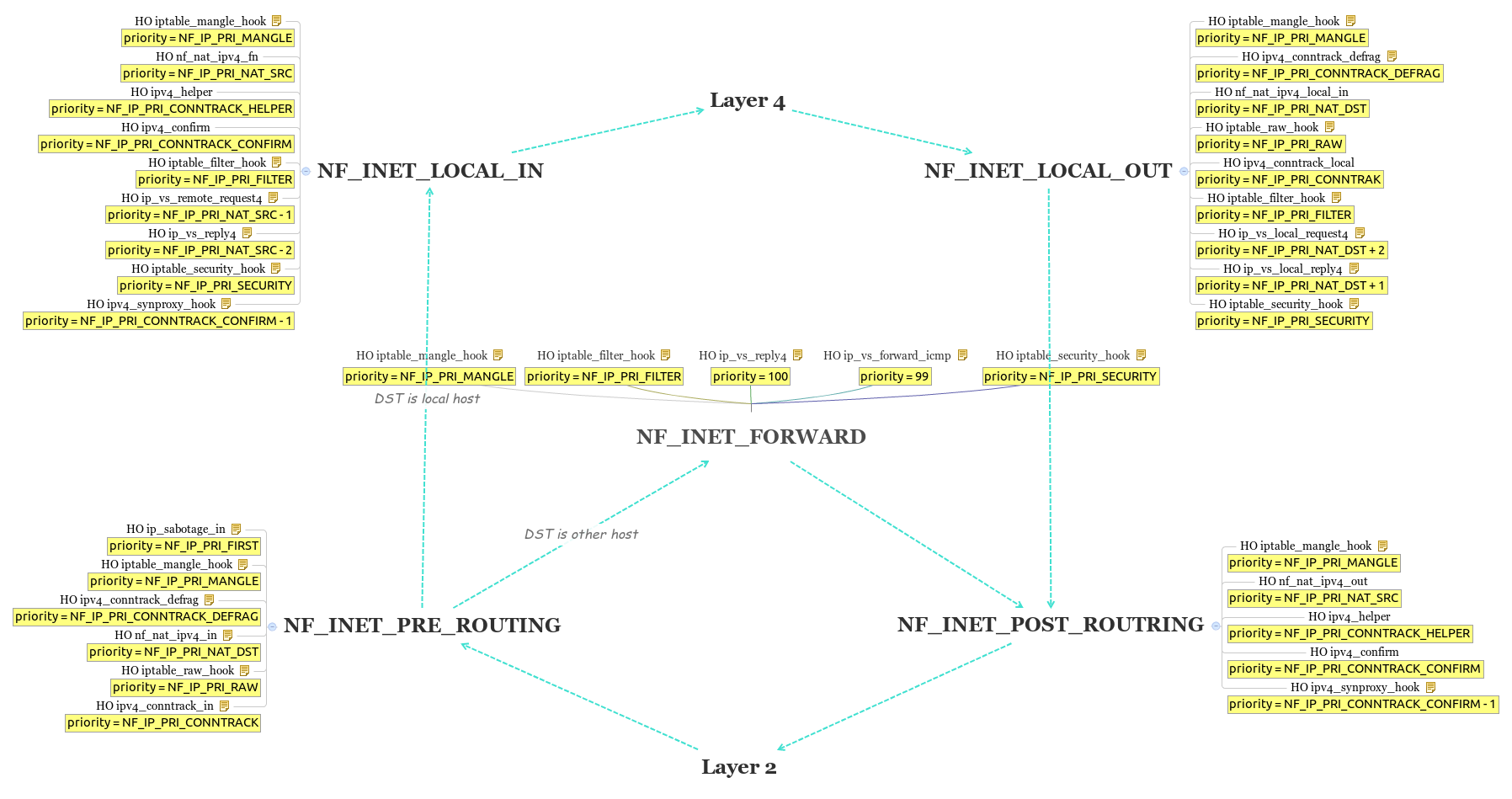
Like layer 2, Layer 3 framework also consists of 5 HOOKs, but they all design based on header information above layer 3, like IP header, TCP header, UDP header. HOOK NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING is the entry point, what it does here are SNAT, classification, more importantly, connection track, after going through, the next thing to do is route table look-up, which determines where packets should route to, the first option is route to local host, packets is delivered up after HOOK NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, which will handle the packets filter, the another option is route to other host, in this routine, packets need to go through HOOK NF_INET_FORWARD for packet filtering, first. The another entry point of layer 3 stack is HOOK NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT, which used for self-generated packets. For packet sent from local host, route table look-up actually happens at layer 4 before packet delivering down, so when packets reach HOOK NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT, it already know where it should route to, so at this HOOK, it will do packet filtering, before packets deliver down, the last HOOK is NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, at this HOOK, it will do DNAT, classification, and connection track.
Before digging into each HOOK, let’s have a look at hook operation priority structure, which defines in file include/uapi/linux/netfiler_ipv4.h:
enum nf_ip_hook_priorities {
NF_IP_PRI_FIRST = INT_MIN,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG = -400,
NF_IP_PRI_RAW = -300,
NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_FIRST = -225,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK = -200,
NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE = -150,
NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST = -100,
NF_IP_PRI_FILTER = 0,
NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY = 50,
NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC = 100,
NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_LAST = 225,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER = 300,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM = INT_MAX,
NF_IP_PRI_LAST = INT_MAX,
};
NF_IP_PRI_FIRST has the highest priority. NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG, NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK, NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER, NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM are used for connection track system, in which ALG embedded with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER. priorities from NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_FIRST to NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_LAST are used fro netfilter module, in iptables chains, mangle table’s priority is NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, NAT table’s priorities are NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST and NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC, and filter table’s priority is NF_IP_PRI_FILTER.
HOOK NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING
There are 6 hook operations registered on this HOOK, ip_sabotage_in with priority NF_IP_PRI_FIRST, iptable_mangle_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, ipv4_conntrack_defrag with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG, nf_nat_ipv4_in with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST, iptable_raw_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_RAW, and ipv4_conntrack_in with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK.
ip_sabotage_in: this hook operation actually is registered in bridge stack, when packets are processing at HOOK NF_BR_PRE_ROUTING, it will experience HOOK NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING once, so if packets’s destination is local host, it will experience HOOK NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING again when delivered up, this hook operation’s existence is help packets skipping this HOOK if they are delivered up from bridge stack, and that is why it has the highest priority.
ipv4_conntrack_defrag: this hook operation is used to handle fragmented packets, they will gather here.
iptable_raw_hook: this hook operation will iterate rules in raw table registered on this HOOK, if it find one match, that rule will be executed, like filter, nat, and mangle, rules on this table, we can configure via command iptables, too, rules on this table have the highest priority in netfilter system as we can check in the priority structure.
ipv4_conntrack_in: this hook operation is the entry point of connection track system, it will create a record for connection if it is the first packet, and it can be tracked, or it will update connection state, or some some protocol specific action like SIP ALG, FTP ALG, etc. Connection is recorded based on network 5 elements: SRC/DST IP address, SRC/DST port, protocol.
iptable_mangle_hook: this hook operation will run all rules in mangle table registered on this HOOK, it is not like NAT, and filter table, which will execute only one rule if find one match, rules in mangle table are packets marking, or TOS setting, which are used to classify packets.
nf_nat_ipv4_in: this hook operation will iterate rules in NAT table registered on this HOOK, if it find one match, that rule will be executed, for one single connection, only the first packet will experience this hook operation, the rest will skip it, that is because once the first packet go through this hook operation, this connection will be track by connection track system, which we can check it via interface /proc/net/nf_conntrack and the hook operations registered by connection track system have higher priority.
After passing through all hook operations, it will start to route table look-up, the result will determine where this packet goes.
HOOK NF_INET_LOCAL_IN
There are 9 hook operations registered on this HOOK, iptable_mangle_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, nf_nat_ipv4_fn with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC, ipv4_helper with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER, ipv4_confirm with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM, iptable_filter_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_FILTER, ip_vs_remote_request4 with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC -1, ip_vs_reply4 with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC -2, iptable_security_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY, and ipv4_synproxy_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM -1.
iptable_mangle_hook: this hook operation, like I mentioned above, is used to packets marking, rules on this HOOK are packets classify for target local host.
iptable_filter_hook: this hook operation is used for packets filtering, the main purpose for rules on this HOOK are prevent unnecessary packets from injecting into local host.
iptable_security_hook: this hook operation will iterate rules in security table registered on this hook, if it find one match, that rule will be executed, and return. Security table, like mangle, NAT, filter, can configure via iptables, too, its functionality is similar with filter, but mainly for MAC rules.
ip_vs_reply4: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, which route packet not by IP address, but service, the combination of IP address and port. operation registered on this hook is used only for virtual server NAT, check if packet is reply for established from remote host.
ip_vs_remote_request4: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, too, its purpose here is schedule and forward packets from remote client.
nf_nat_ipv4_fn: this hook operation is used for rules on NAT table, it do NAT packets from remote host to local host.
ipv4_helper: this hook operation is used for ALG module, which handle private IP address and public address translation for address information hidden in packet content. It usually used in gateway device, when packets in LAN side have private address information in content, like FTP, SIP, gateway will replace its public address with private address, and it will add an entry in /proc/net/nf_conntrack_expect, so when remote clients want to reach services in LAN side, packets will reach this HOOK at gateway, operation on this hook will accept service request and forward request to LAN host.
ipv4_synproxy_hook: this hook operation is registered in syn proxy module, which used to defense DDOS attack, syn proxy will redirect TCP syn packets from client to local host, operation on this hook is accept request for server, and send reply to clients.
ipv4_confirm: this hook operation is registered in connection track module, it aim to confirm connection establishing for packet starting from local host.
After packets pass through this HOOK, it will look-up hash table in raw socket hash table, diagram socket hash table, and stream socket hash table, check if there is any connection established, or service match, and it will deliver to socket’s RX queue if it finds, or it will be dropped.
HOOK NF_INET_FORWARD
There are 5 hook operations registered on this HOOK, iptable_mangle_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, iptable_filter_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_FILTER, ip_vs_reply4 with priority 100, ip_vs_forward_icmp with priority 99, and iptable_security_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY.
iptable_mangle_hook: this hook operation used for rules on mangle table, rules on this HOOK are classify packets from remote host to other host.
iptable_filter_hook: this hook operation used for rules on filter table, rules on this HOOK are related to packets forwarding.
iptable_security_hook: this hook operation used for rules on security table, which rules related to packets forwarding.
ip_vs_forward_icmp: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, in order to catch ICMP related packets destined for 0.0.0.0/0. When fwmark-based virtual service is used, such as transparent cache cluster, TCP packets can be marked and routed to ip_vs_in, but ICMP destined for 0.0.0.0/0 cannot be easily marked and sent to ip_vs_in_icmp. So catch them at this HOOK and send them to ip_vs_in_icmp.
ip_vs_reply4: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, used for virtual server NAT, check if packet is reply for established.
After pass through this HOOK, packets will be delivered to HOOK NF_INET_POST_ROUTING.
HOOK NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT
There are 9 hook operations registered on this HOOK, iptable_mangle_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, ipv4_conntrack_defrag with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG, nf_nat_ipv4_local_in with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST, iptable_raw_hook, with priority NF_IP_PRI_RAW, ipv4_conntrack_local with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK, iptable_filter_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_FILTER, ip_vs_local_request4 with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST +2, ip_vs_local_reply4 with priority NF_IP_NAT_DST +1, and iptable_security_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY.
ipv4_conntrack_defrag: this hook operation is used for fragment packets, it gather fragments from local client.
iptable_raw_hook: this hook operation is used for rules in raw table, whose priority is higher than any other tables in netfilter module.
ipv4_conntrack_local: this hook operation is registered in connection track module, its operation is track connection from local host.
iptable_mangle_hook: this hook operation is used for rules in mangle table, it classify packets from local host.
nf_nat_ipv4_local_in: this hook operation is used for rules in NAT table, it do NAT for packets from local host.
ip_vs_local_reply4: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, used for virtual server NAT, check if packet is reply for established from local host.
ip_vs_local_request4: this hook operation is registered in module IP virtual server, used for schedule and forward packet from local clients.
iptable_filter_hook: this hook operation is used for rules in filter table, it filter unnecessary packets generated from local host.
iptable_security_hook: this hook operation is used for rule in security table, it apply MAC rules for packets from local host.
After packets pass through this HOOK, they will be delivered to HOOK NF_INET_POST_ROUTING.
HOOK NF_INET_POST_ROUTING
There are 5 hook operations registered on this HOOK, iptable_mangle_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE, nf_nat_ipv4_out with priority NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC, ipv4_helper with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER, ipv4_confirm with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM, and ipv4_synproxy_hook with priority NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM -1.
iptable_mangle_hook: this hook operation is used for rules in mangle table, rules for setting TOS value or mark before packet send out.
nf_nat_ipv4_out: this hook operation is used for rules in NAT tables, aim to change source before packets send out.
ipv4_helper: this hook operation used for ALG module, it replace gateway’s public address with LAN host’s private address in packet content, and add an entry in /proc/net/nf_conntrack_expect, which used for accepting service request from remote client, and service request forwarding.
ipv4_synproxy_hook: this hook operation is registered in syn proxy module, operation here is prevent connection from tracked by connection track module, and when connection established, it redirect this request to real server.
ipv4_confirm: this hook operation is registered in connection track module, it is used to confirm connection establishing.
After packets pass through this HOOK, they will be delivered down to layer 2.
How packets send out ?
After pass through all HOOKs in layer 3, if packet size is bigger than MTU, it will be fragmented first, and then check the neighbor information, fill IP header information, deliver packets to dev_queue_xmit.
Conclusion
This is the basic framework of layer 3, and I don’t focus on much details, there are many sub-systems, like route, ALG, connection track, IP virtual server, netfilter, etc, they all designed based on this basic framework, I will talk about them in detail when I get time.
